Charles Thomson Rees Wilson (1869-1959) received the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1927 for his invention of the Cloud Chamber.

This is Wilson's original design of the cloud chamber.
The cloud chamber is a device that makes visible the paths of particles emitted as a result of radioactive decay. This device detects elementary particles and other ionizing radiation, which is radiation that have enough energy to cause atoms to lose electrons and become ions.
This device lead to the discovery of the positron (a positively charged electron), the first observed form of antimatter.
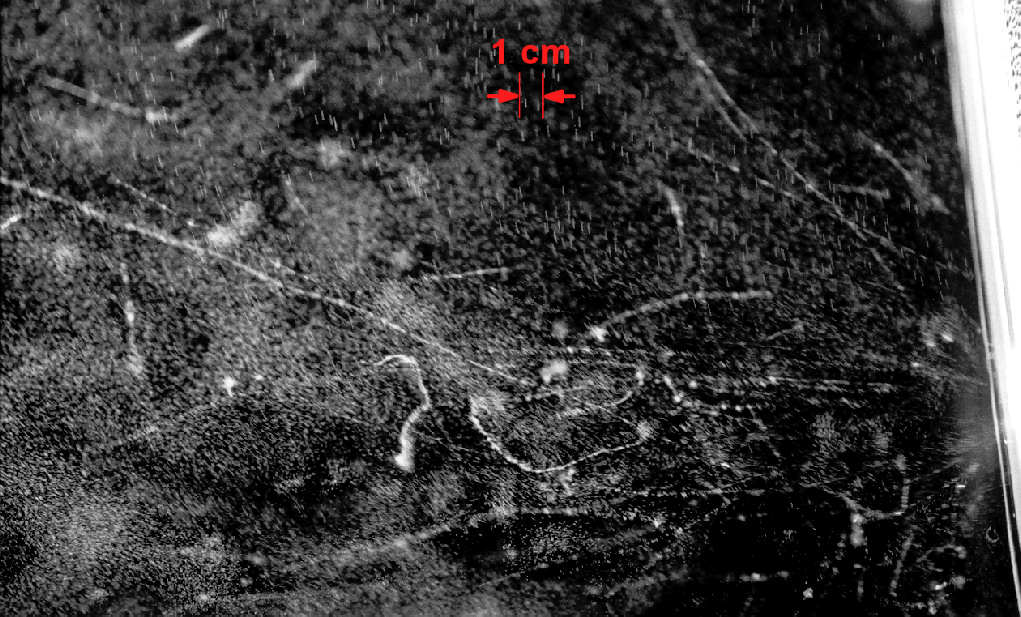
The cloud chamber is used for study in radioactivity. Physicist observe particle trails and properties. It is extremely important in cosmic ray research. Cosmic rays are energetic particles originating from outer space.

This image is one of the first cloud chamber photographs showing the track of a cosmic ray.

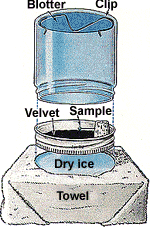
What happens in the cloud chamber?
1. The top of chamber is at room temperature and the bottom is very cold because of the dry ice.
2. The alcohol evaporates from felt and slowly sinks down to the bottom
3. The chamber is saturated with alcohol vapor (the gaseous form of alcohol) because of methyl alcohol
4. Since the bottom is very cold, once the vapor has fallen, it is in a supercooled state... the alcohol is in vapor form, but at a temperature where vapor normally cannot exist.
5. Therefore, vapor will easily condense into liquid form.
6. When a charged particle comes along, it IONIZES the vapor... it tears away the electrons in some of the gas atoms along its path.
7. This leaves these atoms positively charged.
8. Nearby atoms are attracted to this ionized atom.
9. Condensation process begins.
10. You see little droplets forming along the path the particle took through the chamber.
*The atmosphere of the cloud chamber is supersaturated.
Supersaturated definition:
-being more concentrated than normally possible and therefore not in equilibrium
-The solvent is holding more solute than it should at a given temperature
The supersaturated atmosphere in this device is maintained continuously by the evaporation of methyl alcohol at room temperature.
Cloud chamber is based on the principal of Condensation Nuclei:


 : alpha particles
: alpha particles
Beta particles:
-Less clear, light, wispy, irregular trails
-The tracks made by low energy beta are thicker than the tracks of high energy beta
-Low energy beta tracks also tend to wiggle. Beta particles have a small mass compared with an air molecule so it is easily deflected : Low energy beta particles
: Low energy beta particles
: High and Low energy beta particles
Gamma Rays:
-Causes only one ionization and then disappears
-Gamma is only emitted as a result of alpha or beta radiation
-Gamma ionization tends to happen in the wall or floor of the chamber rather than in the air
-Random directions... not directly from the radioactive source : Gamma ray
: Gamma ray
--When any uniform magnetic field is applied across the cloud chamber, positively and negatively charged particles will curve in opposite directions
Pictures of particle trails:
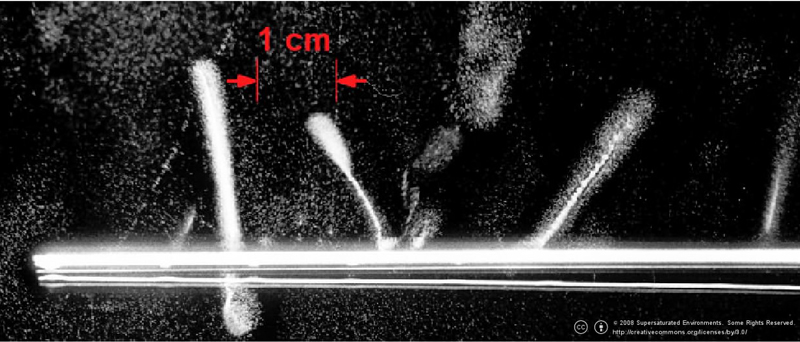
alpha paricle
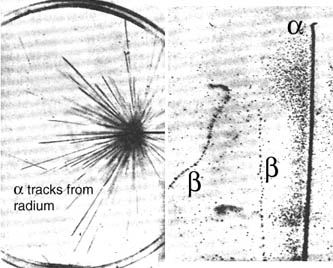
This image was obtained by Wilson. It shows both alpha and beta particles.